Dehydrogenation of alcohol
When the vapours of an alcohol are passed over copper catalyst heated at 573K. it undergoes dehydrogenation (loss of hydrogen or oxidation). The product formed depends on the alcohol and hence this reaction is also used to distinguish the three classes of alcohols.
When the vapours of a primary alcohol are passed over copper heated at 573K, the correspondingaldehyde is formed.
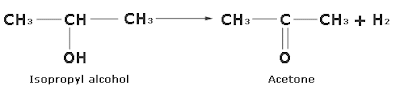
When the vapours of a secondary alcohol are passed over copper heated at 573K, the corresponding ketone is formed.
Tertiary alcohol when reacted with copper catalyst at 573K are not dehydrogenated but undergoes dehydration to give the corresponding alkene.
When the vapours of a primary alcohol are passed over copper heated at 573K, the correspondingaldehyde is formed.
When the vapours of a secondary alcohol are passed over copper heated at 573K, the corresponding ketone is formed.
Tertiary alcohol when reacted with copper catalyst at 573K are not dehydrogenated but undergoes dehydration to give the corresponding alkene.
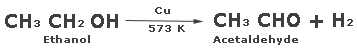


Comments
Post a Comment