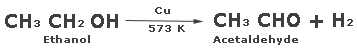Extraction of copper from copper pyrites (CuFeS2)

Copper is extracted from its principal ore copper pyrites (CuFeS 2 ). The ore is concentrated by froth flotation process. The concentrated ore is roasted in a reverberatory furnace when the following reactions occur. 1. The volatiles like sulphur and arsenic escape as gases S + O 2 --------------> SO 2 4AS + 3O 2 --------------->2AS 2 O 3 2. Copper pyrites is converted to a mixture of Cu 2 S and FeS 2CuFeS 2 + O 2 ---------------> Cu 2 S + 2FeS + SO 2 3. The sulphides of Cu and Fe are partially oxidized 2Cu 2 S + 3O 2 <=======> 2Cu 2 O + 2SO 2 2FeS + 3O 2 <========> 2FeO + 2SO 2 Smelting in extraction of copper The roasted ore mixed with silica as flux is heated in a blast furnace by a blast of hot air. Most of the FeO is removed as a slag and a molten mixture of Cu 2 S and FeS called matte, get collected in the hearth of the furnace. ...